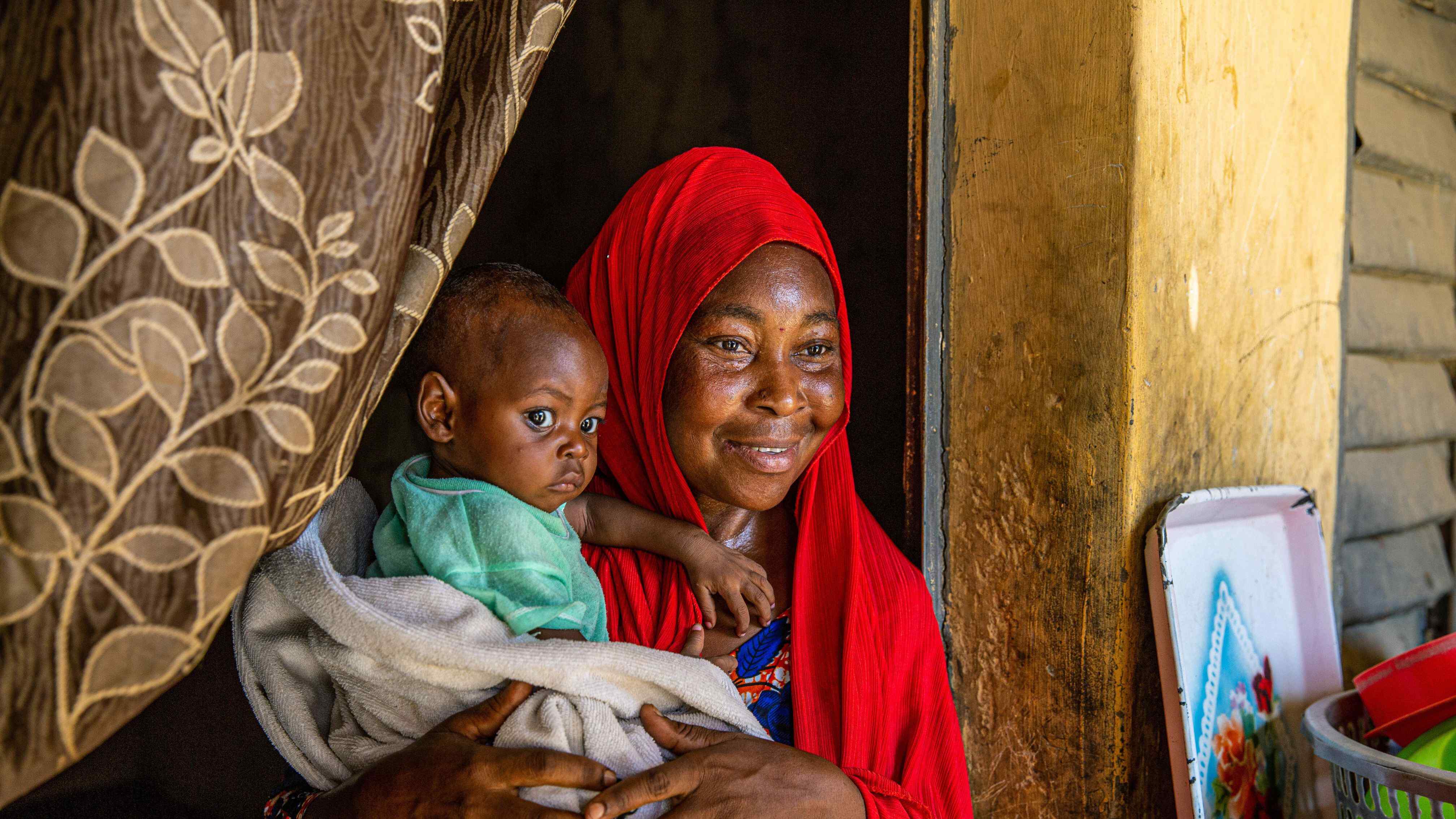
IRC calls for urgent climate action for Nigeria
- The IRC is urging for fragile and conflict-affected countries like Nigeria, which is facing unprecedented flooding, to be prioritized in the global climate agenda at COP28.
- Cholera outbreaks have increased due to devastating flooding last year, with 23,550 suspected cases reported in 31 states, especially Borno with 12,000 cases.
- In July this year, flood alerts were issued in multiple Nigerian states, necessitating concrete commitments to unlock more funding for adaptation and climate resilience.
Country facts
- Population: 196 million
- People internally displaced by crisis: Over 2.1 million
- Population in need of humanitarian aid: 10.6 million
- Rank in Human Development Index: 158 of 189
IRC response
- Started work in Nigeria: 2012
- People assisted in 2019: Over 1.3 million
- People we hope to reach per year: 1.5 million
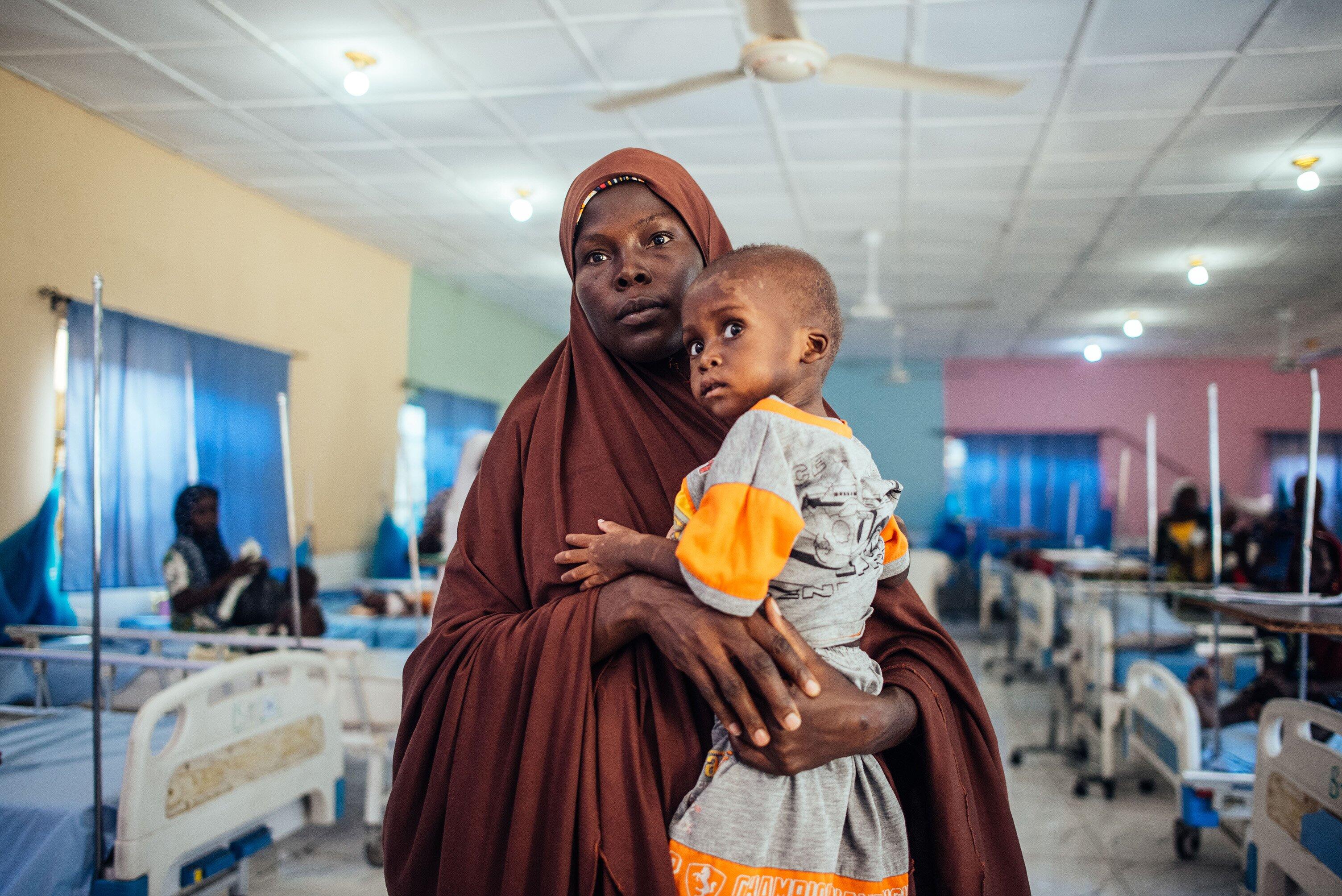
Nigeria, the most populous country in Africa, has endured decades of political instability and economic inequality. Ongoing violence continues to force people to flee their homes in the northeast and other conflict zones to seek safety in other parts of the country. The IRC provides displaced Nigerians and vulnerable host communities in the northeast with access to health care, nutrition, sanitation and education.
Nigeria is a diverse country with areas of great wealth and profound poverty. Despite massive oil revenues, nearly two-thirds of Nigeria’s population lives in poverty, especially in the marginalised and underserved northern and northeastern regions. The country’s vulnerability to drought, flooding and other forms of extreme weather also contributes to the chronic malnutrition and frequent outbreaks of disease that have affected more than 13.5 million people.
Although decades of military rule ended when Nigeria regained democracy in 1999, the country has been plagued by political, economic and social challenges that threaten the consolidation of gains made since its transition to civilian government.
Since 2014, the world’s deadliest militant group, Boko Haram, has killed thousands of people, abducted thousands of women and children, and uprooted over 2.5 million people. Many Nigerians who fled to neighbouring Chad, Cameroon and Niger have been forced to return because of deteriorating conditions in those nations. Well over 2 million people have been internally displaced: the continuous conflict has forced people to live in camps in the outskirts of towns of Borno state, where they are enduring violence, poverty and constant insecurity.
Although Nigeria is one of Africa's leading oil producers, more than half its population lives in poverty. Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of people in need of humanitarian assistance in northeast Nigeria has spiked to 10.6 million, with another 3.8 million struggling to access enough food.
There are now over 2 million displaced people in the northeast, where the hunger crisis has reached emergency levels. These uprooted families are in acute need of food, clean water, shelter, education and health care. The conflict has led to the destruction of 66 % of health facilities in Borno, Adamawa and Yobestates.
Just 8% of this displaced population lives in official camps and receives government support. Children who have lost parents to the conflict or have been separated from family are especially vulnerable. Women and girls have been subjected to sexual violence and enslavement. The COVID-19 pandemic has only worsened the situation: families have lost their livelihoods, falling into deeper poverty, and health facilities have been stretched beyond capacity.
Funding needed to address the magnitude of the humanitarian situation in Nigeria is falling short. Humanitarian responders have been able to reach only a fraction of people in desperate need.
Although Nigeria is one of Africa's leading oil producers, more than half its population lives in poverty. Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of people in need of humanitarian assistance in northeast Nigeria has spiked to 10.6 million, with another 3.8 million struggling to access enough food.
There are now over 2 million displaced people in the northeast, where the hunger crisis has reached emergency levels. These uprooted families are in acute need of food, clean water, shelter, education and health care. The conflict has led to the destruction of 66 % of health facilities in Borno, Adamawa and Yobestates.
Just 8% of this displaced population lives in official camps and receives government support. Children who have lost parents to the conflict or have been separated from family are especially vulnerable. Women and girls have been subjected to sexual violence and enslavement. The COVID-19 pandemic has only worsened the situation: families have lost their livelihoods, falling into deeper poverty, and health facilities have been stretched beyond capacity.
Funding needed to address the magnitude of the humanitarian situation in Nigeria is falling short. Humanitarian responders have been able to reach only a fraction of people in desperate need.
Ensuring people are protected from violence and have access to enough food remains critical: a large percentage of the population suffers from malnutrition. Women, girls and other vulnerable groups are subject to exploitation and abuse, and children often have no access to education.
The global humanitarian response to the crisis in Nigeria has been insufficient to serve the millions of people displaced by violence and natural disasters. Sustainable gains in Nigeria will require not only increased aid but new emphasis on helping people affected by crisis to earn enough income to meet their basic needs. Improving the economic wellbeing of women and girls will be a particular focus for the IRC over the next few years.
Download the IRC's Nigeria strategy action plan to learn more about our programme priorities.
The violent seven-year conflict originating in Nigeria has intensified in the last three years and spread across borders into Chad, Niger and Cameroon, causing a growing humanitarian crisis in a region known as the Lake Chad Basin. Read recommendations from the IRC and other aid groups working in the region.